Similar to how industrial automation is improving processes and data collection, we are witnessing a technological revolution that amplifies this application, IIoT or Industrial IoT, the Industrial Internet of Things. Alongside industrial computing trends, connectivity technology is combined, opening up a world of possibilities for the industry.
The IIoT: intelligent connectivity driving the industry
Today, there are around 4.6 billion people connected to the internet, but there are even more – it’s estimated that over 30 billion devices are connected to the internet, interacting without human intervention. When this happens, it’s called the Internet of Things (IoT). A clear example of this is a smart fridge that places orders for items when it detects they are running low. It’s a practical and illustrative example, but when we look within the industry, we find much more productive processes that have become a cornerstone of the fourth industrial revolution. According to Oxford Economics data, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) can impact industries that represent 62% of the GDP in G20 countries.
The foundation of IIoT or Industrial IoT
IIoT is based on the interconnection of machines, sensors, and autonomous systems in the industrial environment. These devices are designed to collect real-time data and transmit it through secure networks for analysis and use. This real-time data collection capability is essential for informed decision-making and process optimization. With this data, they can make programmed and automated decisions, even improving their own processes and identifying errors or inefficiencies.
The role of the Panel PC in IIoT solutions
The role of a Panel PC in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is essential for the operation and management of this technological ecosystem. These industrial computers, available in various formats and sizes depending on the industry and application, perform several key functions in IIoT:
- Data Collection and Processing: Computers, whether cloud servers or local IoT gateways, are responsible for collecting data from scattered sensors and IoT devices. This data can include various types, such as temperature, humidity, motion, etc. Once collected, PCs process this data for analysis..
- Data Analysis: The ability to analyze large volumes of data is crucial in IIoT. Computers use data analysis algorithms and techniques to extract valuable information, detect patterns, anomalies, or trends, and convert data into knowledge that can be used for decision-making.
- Device Management: PCs are responsible for managing the communication and control of IoT devices. This includes tasks such as initial configuration, firmware updates, IP address assignment, and connectivity management.
- Security: Security is a critical aspect of IIoT. Panel PCs implement security measures to protect both transmitted data and the devices themselves. This includes authentication, data encryption, access control, and cyber threat detection.
- Interconnection: Industrial computers enable the interconnection of IoT devices through communication protocols such as MQTT, HTTP, or CoAP. This allows devices to communicate with each other and with centralized management systems.
- Storage: Data generated by IoT devices can be voluminous. Computers can securely and efficiently store this data, either locally or in the cloud, for later access and analysis.
- Data Presentation: Panel PCs also play a role in data presentation. They can display information through graphical user interfaces (GUI) or web applications, allowing end-users to visualize and understand the data generated by IoT devices.
- Automation and Control: Computers can receive data from IIoT and make automated decisions based on that data. This is used in applications such as home automation, supply chain management, and industrial automation.
Benefits of IoT solutions for the industry
- Greater Operational Efficiency: IIoT enables companies to monitor and control their operations more effectively. Sensors can detect performance problems in real-time and trigger alerts, allowing for an immediate response to prevent costly production disruptions.
- Improved Machine Performance: A clear example of a solution is a machine that goes from being stopped to full operation. This represents a loss of revenue with high consumption. Therefore, IIoT can process this data to optimize utilization and production time to spend less and avoid machine downtime.
- Predictive Maintenance: IIoT systems can predict when a machine will need maintenance before it fails. This reduces maintenance costs, minimizes unplanned downtime, and extends the equipment’s lifespan
- Reduced Human Errors: With data collection that provides forecasting capability and connects operators to the IIoT ecosystem, it becomes much more challenging for errors to occur, saving time for staff.
- Improved Product Quality: The ability to monitor and adjust processes in real-time with IIoT ensures greater consistency in product quality. This is especially valuable in industries such as manufacturing and food production.
- Cost Reduction: IIoT can help identify inefficiencies in processes, reducing resource wastage and saving costs. Additionally, by optimizing energy management and material usage, significant savings can be achieved.
- Seamless Traceability: Products stored and in transit are connected through automatic data capture, allowing us to have real-time information on them: status, location, conditions, environment, etc.
Examples of IoT or IIoT Solutions
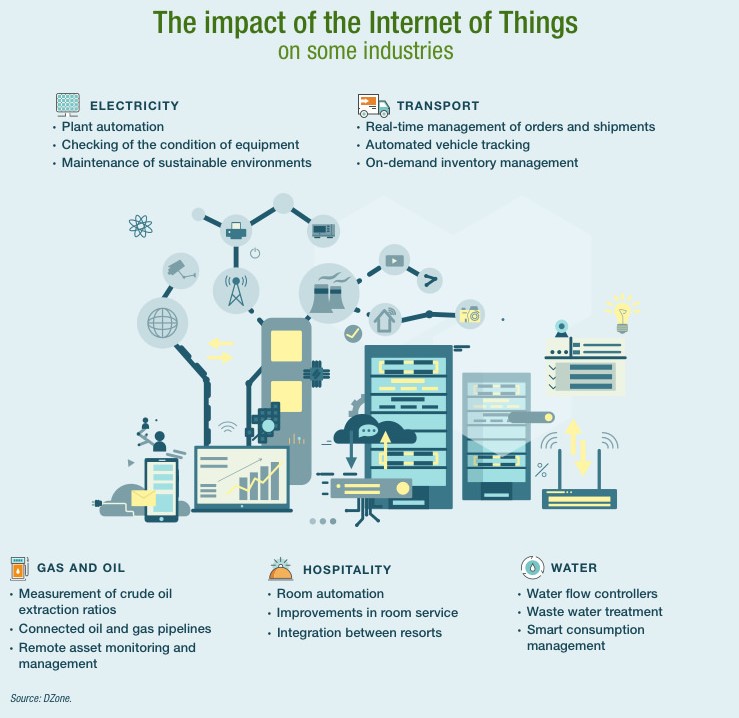
In the future, we will see many more solutions in the Industrial IoT, both for consumers and industries. It is estimated that investment in this area will double in 2025, especially in the industry for the use of robots or cobots, predictive maintenance, security, and process efficiency. Below is an infographic of the most common real-world cases in some sectors today.